
Researchers suggest that these exchanges may be a response to DNA damage during the copying process. Sister chromatids occasionally exchange small sections of DNA during this time, a process known as sister chromatid exchange. The copied DNA from each chromosome is arranged into two identical structures, called sister chromatids, which are attached to one another during the early stages of cell division. When a cell prepares to divide to form two cells, the DNA that makes up the chromosomes is copied so that each new cell will have two copies of each chromosome, one from each parent. Because RecQ helicases help maintain the structure and integrity of DNA, they are known as the "caretakers of the genome."
This unwinding is necessary for several processes in the cell nucleus, including copying (replicating) DNA in preparation for cell division and repairing damaged DNA. Helicases are enzymes that attach (bind) to DNA and unwind the two spiral strands ( double helix ) of the DNA molecule.

The BLM gene provides instructions for making a member of a protein family called RecQ helicases. Mutations in the BLM gene cause Bloom syndrome. Women with the disorder generally have reduced fertility and experience menopause at an earlier age than usual. Men with Bloom syndrome usually do not produce sperm and as a result are unable to father children (infertile). Other features can include learning disabilities, an increased risk of diabetes, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and mild immune system abnormalities leading to recurrent infections of the upper respiratory tract, ears, and lungs during infancy. Individuals with Bloom syndrome have a high-pitched voice and distinctive facial features including a long, narrow face a small lower jaw and prominent nose and ears. They can develop any type of cancer, but the cancers arise earlier in life than they do in the general population, and affected individuals often develop more than one type of cancer. People with Bloom syndrome have an increased risk of cancer.
Bloom syndrome skin#
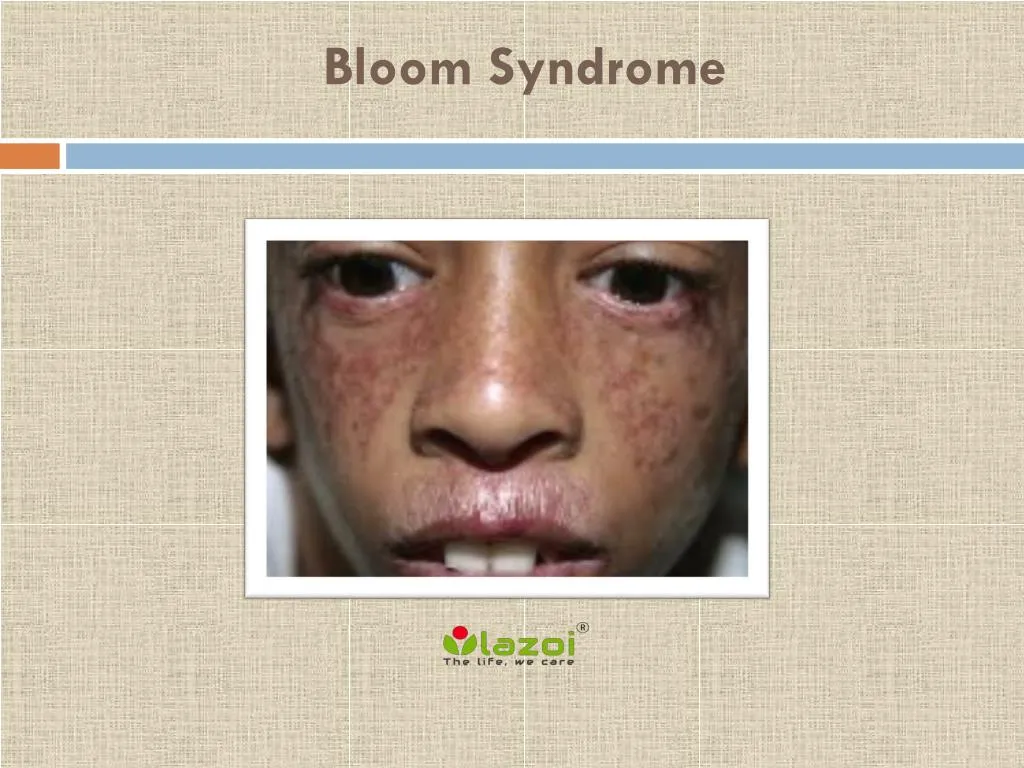
These patches appear on areas of the skin that are not exposed to the sun, and their development is not related to the rashes. Other skin features include patches of skin that are lighter or darker than the surrounding areas (hypopigmentation or hyperpigmentation respectively). Small clusters of enlarged blood vessels (telangiectases) often appear in the rash telangiectases can also occur in the eyes. A skin rash can also appear on other areas that are typically exposed to the sun, such as the back of the hands and the forearms.
Bloom syndrome Patch#
People with Bloom syndrome are usually smaller than 97 percent of the population in both height and weight from birth, and they rarely exceed 5 feet tall in adulthood.Īffected individuals have skin that is sensitive to sun exposure, and they usually develop a butterfly-shaped patch of reddened skin across the nose and cheeks. Bloom syndrome is an inherited disorder characterized by short stature, a skin rash that develops after exposure to the sun, and a greatly increased risk of cancer.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
